Curious about the drawbacks of having a weather station? Look no further! In this article, we explore the disadvantages of these nifty devices.
From limited accuracy and maintenance challenges to potential reliance on external sources, we uncover the downsides of owning a personal weather station.
So, if you’re considering investing in one, stay tuned to discover what might work against you when monitoring the weather conditions from the comfort of your home.
This image is the property of slideplayer.com.
Review contents
1. Limited accuracy
1.1 Inaccurate measurements
One of the significant disadvantages of weather stations is their limited accuracy when measuring weather conditions. While these devices are designed to provide reliable information, there can be variations in the accuracy of measurements. Factors such as sensor calibration, environmental conditions, and potential wear and tear of the equipment over time can all contribute to inaccuracies in the data collected by weather stations.
1.2 Unpredictable data
Weather is a complex and dynamic phenomenon, so it can be challenging to predict accurately. Weather stations use various sensors to measure temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation. However, due to the inherent unpredictability of weather patterns, there can be instances where the collected data does not accurately represent the actual weather conditions. This inconsistency in data can lead to challenges in making precise weather forecasts or analyzing long-term weather patterns.
1.3 Potential for malfunction
Weather stations are technical devices, and like any other piece of equipment, they can experience malfunctions. Factors such as electronic failures, sensor errors, or physical damage can impact the performance of a weather station. When a malfunction occurs, it can lead to incorrect measurements or even a complete loss of data. This potential for malfunction highlights the importance of regular maintenance and monitoring of weather stations to ensure their reliability and accuracy.
2. High cost
2.1 Initial investment
One of the significant drawbacks of weather stations is their high initial investment cost. Setting up a weather station involves purchasing equipment, such as sensors, data loggers, and weather monitoring software. The installation process may also require professional assistance or specialized tools, adding to the overall cost. This can be a barrier for individuals or organizations with limited financial resources who wish to establish a weather station.
2.2 Maintenance expenses
Apart from the initial investment, weather stations also incur ongoing maintenance expenses. Regular calibration of sensors, periodic software updates, and system checks are essential to maintain the accuracy and functionality of the weather station. Additionally, weather stations may require occasional repairs or replacement of faulty components, which can add to the overall maintenance costs over time.
2.3 Replacement parts
Over time, the components of a weather station may wear out or become obsolete. The availability of replacement parts can be challenging, especially for older or less common models. This can result in difficulties when attempting to repair or upgrade a weather station, potentially leading to increased costs or even the need to replace the entire system.
3. Data limitations
3.1 Limited range
Weather stations are typically designed to monitor weather conditions within a specific range. This range limitation means that the collected data may not accurately represent weather conditions in areas beyond the reach of the weather station’s sensors. As a result, there may be gaps in weather information, especially in remote or less populated regions where weather stations might be scarce.
3.2 Spatial variability
Weather conditions vary significantly across geographical locations, even within relatively small areas. However, weather stations may not capture these spatial variations accurately due to their limited coverage area.
This can pose challenges when analyzing local weather patterns or making localized weather predictions, as the data collected by a single weather station may not always reflect the conditions experienced in nearby areas.
3.3 Missing or incomplete data
Weather stations rely on continuous measurements to provide accurate and reliable weather information. However, various factors can lead to missing or incomplete data. For example, technical issues with sensors or data loggers can result in gaps in the collected data. Additionally, extreme weather events or environmental conditions may affect the functioning of the weather station, leading to temporary or permanent data losses. Such limitations hinder the availability of comprehensive and continuous weather data for analysis and forecasting.
4. Vulnerability to environmental factors
4.1 Damage from extreme weather
Weather stations are exposed to the same environmental conditions they aim to monitor. This exposure makes them susceptible to damage from extreme weather events such as hurricanes, thunderstorms, or heavy snowfall. Strong winds can cause structural damage or displace sensors, affecting the accuracy and functionality of the weather station. Heavy rainfall or snow accumulation can also damage water, potentially rendering the entire system inoperable.
4.2 Interference from nearby structures
The placement of a weather station can significantly impact its performance. Nearby structures or vegetation can cause interference with wind measurements, leading to inaccurate data.
Tall buildings, trees, or hills can create turbulence or sheltered areas that distort wind patterns, compromising the reliability of wind speed and direction measurements. Considering the surrounding environment when installing a weather station is crucial to minimize potential interference.
4.3 Degradation due to environmental conditions
Continuous exposure to environmental conditions can cause degradation of the weather station over time. High temperatures, humidity, or corrosive elements in the air can impact the integrity and functionality of the equipment. Components such as sensors, cables, or connectors may deteriorate or become less reliable, potentially affecting the accuracy of the collected weather data. Regular inspections and maintenance are necessary to mitigate these effects and ensure the longevity of the weather station.
This image is the property of image.slidesharecdn.com.
5. Dependency on power source
5.1 Reliance on Electricity
Weather stations require a stable and continuous power supply to operate effectively. Most weather stations are electrically powered and directly connected to a power source or a battery system. This reliance on electricity can be a drawback, particularly in areas prone to power outages or limited access to electricity. Without a reliable power source, the weather station may cease functioning, resulting in data gaps and a loss of real-time weather monitoring capabilities.
5.2 Power outage concerns
In a power outage, weather stations not equipped with backup power systems may be rendered useless. Extended power outages can disrupt weather data collection, potentially impacting the availability of accurate and timely weather information. It is crucial to have contingency plans, such as backup generators or battery-powered systems, to ensure uninterrupted operation during power outages.
5.3 Need for backup generators
Some weather stations are equipped with backup generators to mitigate the risks associated with power outages. While backup generators can provide temporary power during outages, they come with their own set of challenges. Acquiring and maintaining backup generators can add to the overall cost of the weather station, and periodic fuel refilling or generator maintenance may be required. The need for backup power options emphasizes the importance of reliable energy sources for weather station operations.
6. Limited portability
6.1 Fixed installation
Weather stations are typically designed for fixed installations, so they cannot be easily relocated. Once installed, moving a weather station requires significant effort and resources, from disassembling and reassembling the equipment to reinstalling sensors and calibrating the system. This lack of portability can be a drawback, as it limits the flexibility to monitor weather conditions in different locations or respond to changing monitoring needs.
6.2 Difficulty in relocating
Due to their fixed installation nature, relocating a weather station can be challenging. It involves meticulous planning, coordination, and often the need for professional assistance. Additionally, moving a weather station to a new location may introduce new environmental factors or interferences that were not present in the previous installation site, potentially impacting the accuracy and reliability of the collected weather data.
6.3 Limited coverage area
The limited coverage area of a weather station can be a drawback, especially in regions with diverse topography or large spatial extents. Weather conditions outside the range of a weather station’s sensors may not be accurately captured or represented in the collected data. This limitation can hinder comprehensive weather monitoring and forecasting efforts, particularly in areas with complex weather patterns or significant variations in climatic conditions.
This image is the property of image.slidesharecdn.com.
7. Technological limitations
7.1 Signal range limitations
Weather stations rely on wireless communication technologies to transmit data from sensors to a data logger or a central monitoring system. However, these wireless signals have a limited range, so weather station components need to be nearby for seamless communication. This limitation can restrict the placement of sensors or the central system, potentially compromising the accuracy and effectiveness of data transmission.
7.2 Interference with other electronic devices
In environments where multiple electronic devices are present, there is a potential for interference with the functioning of a weather station. Other wireless devices operating on similar frequencies or electromagnetic interference from nearby electronic equipment can disrupt the operation of the weather station, leading to data inconsistencies or signal loss. Careful consideration of the surrounding electronic environment is necessary to minimize the risk of interference.
7.3 Compatibility issues with software
Weather stations often require software applications or platforms to process, visualize, and analyze the collected data. However, compatibility issues between different software systems can arise, leading to data management and integration challenges. The need for specific software versions or compatibility updates can pose difficulties in seamlessly integrating a weather station into existing data management systems or workflows.
8. Steep learning curve
8.1 Complexity of setup and operation
Setting up and operating a weather station can involve a steep learning curve. The process may require technical skills and knowledge to correctly install sensors, ensure proper calibration, and configure the data logging system. Additionally, operating the weather station and understanding the collected data may require familiarity with meteorological concepts and interpretation techniques. The complexity associated with the setup and operation can be a barrier for individuals without specialized training or expertise.
8.2 Technical knowledge required
A certain level of technical knowledge is necessary to effectively manage and maintain a weather station. This includes understanding the functioning of sensors, troubleshooting potential issues, and interpreting data patterns.
It can be challenging to address malfunctions, calibrate sensors, or make educated decisions based on the collected weather data without proper technical knowledge. Ongoing training and support may be required to ensure the effective operation of the weather station.
8.3 Training and expertise needed
Operating a weather station effectively often requires specific training and expertise in meteorology, data analysis, and instrumentation. Individuals or organizations setting up a weather station without the necessary training may struggle to interpret the collected data accurately or make informed decisions based on the weather information. Investment in training programs or partnering with experienced meteorologists can help bridge the knowledge gap and ensure the successful operation of the weather station.
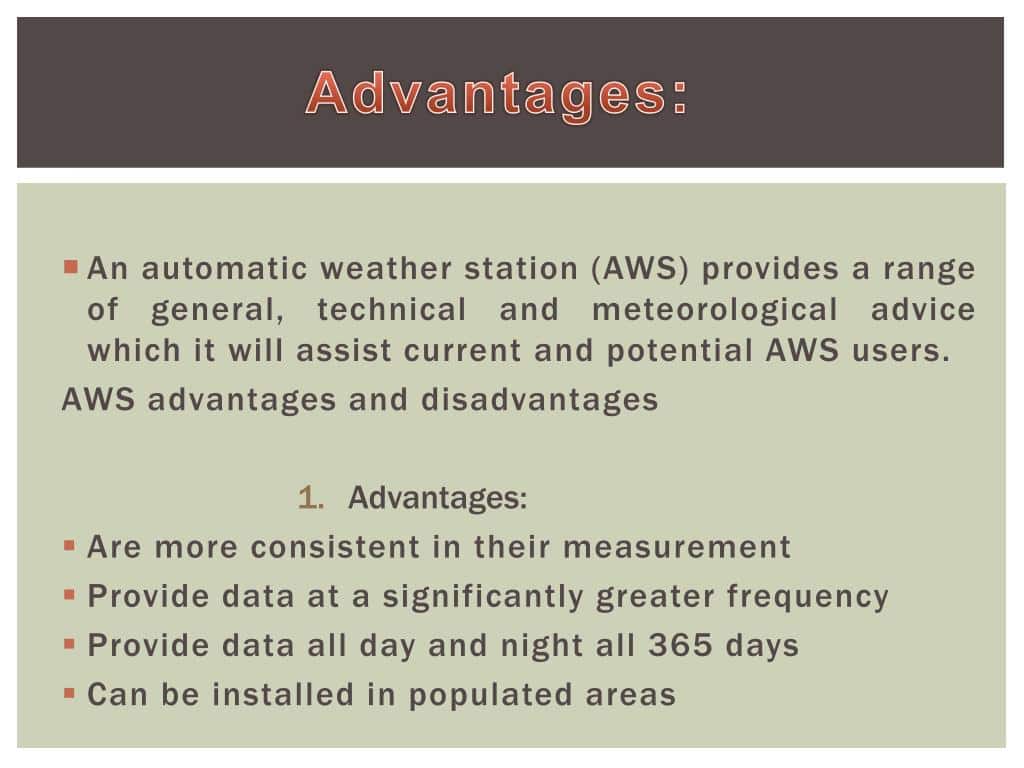
This image is the property of slideplayer.com.
9. Limited functionality
9.1 Lack of advanced features
Weather stations may lack advanced features and capabilities compared to more sophisticated weather monitoring systems. They often focus on measuring basic weather parameters such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed. At the same time, more complex phenomena like atmospheric pressure patterns or air quality measurements may not be included. The limited functionality of weather stations may limit their utility in specific applications or research settings that require more comprehensive data collection.
9.2 Limited integration capabilities
Weather stations are designed as standalone systems, and integrating them with other data sources or applications can be challenging.
The lack of standardized data formats or protocols can hinder seamless integration with existing weather databases or monitoring networks. This limitation can impede efforts to create comprehensive and integrated weather information systems, especially when multiple weather stations must be interconnected.
9.3 Inability to monitor certain weather conditions
Weather stations have inherent limitations when it comes to monitoring certain weather conditions. For example, they may not measure specific phenomena such as lightning strikes, air pollution, or solar radiation. This inability to monitor certain weather conditions restricts the scope of data collection. It may require additional specialized equipment or integrating data from external sources to comprehensively understand the weather.
10. Ethical concerns
10.1 Invasion of privacy
Weather stations installed in residential areas or public spaces can raise concerns about privacy invasion. These stations may capture environmental data and information about nearby individuals or their activities.
While the primary purpose of weather stations is to monitor weather conditions, the unintended collection of personal or sensitive information can be a source of ethical concern. Proper data anonymization and privacy protection measures should be in place to address these concerns.
10.2 Data security and privacy risks
With the increasing reliance on digital data collection and transmission, weather stations face data security and privacy risks.
The stored or transmitted weather data can be vulnerable to cyber threats or unauthorized access, potentially compromising the integrity or confidentiality of the collected information. Weather stations must implement robust security protocols and encryption measures to protect data and prevent unauthorized data access or tampering.
10.3 Misinterpretation of collected data
Interpreting weather data collected by weather stations requires expertise and knowledge of meteorological principles. Misinterpreting collected data by inexperienced personnel or untrained individuals can lead to inaccurate analysis or incorrect conclusions.
This can have significant implications in applications such as weather forecasting, climate research, or decision-making processes that rely on accurate weather information. Proper training and quality control measures are essential to minimize the risks of misinterpretation and ensure the reliability of weather data analysis.
This image is the property of image1.slideserve.com.