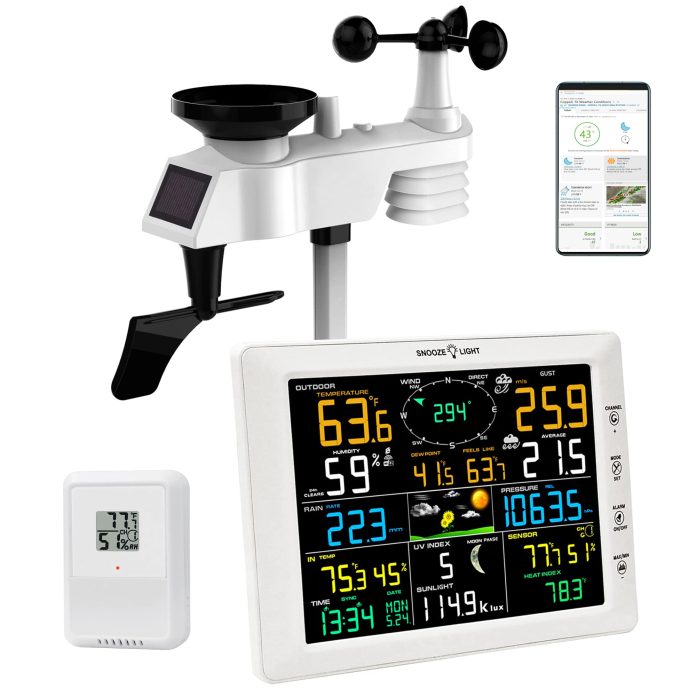
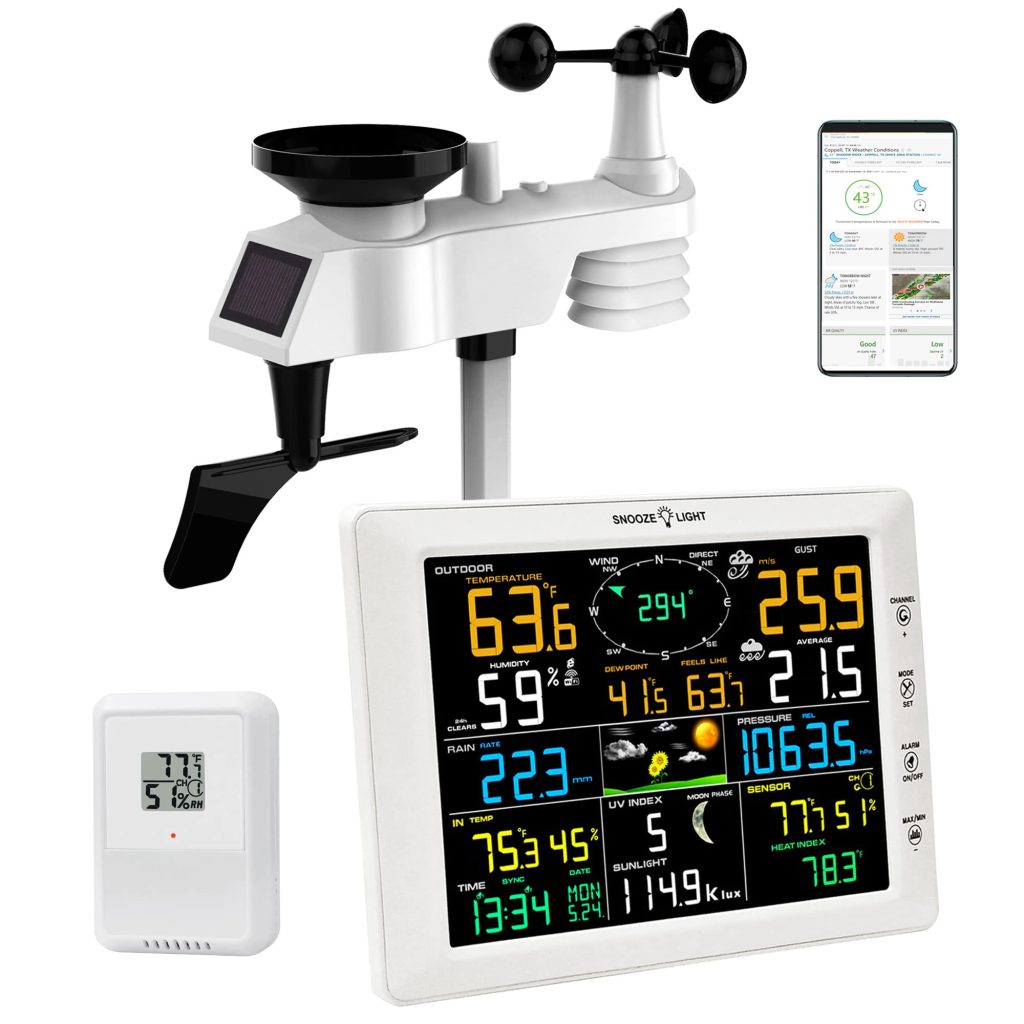
So you’ve decided to invest in a wireless weather station, but you’re left wondering whether you need an Internet connection.
Well, fret not! In this article, we’ll show you whether the Internet is necessary or a luxury for these cutting-edge weather-monitoring devices.
Whether you’re a weather enthusiast or simply looking to upgrade your home weather station, read on to discover all you need to know about the Internet requirements for wireless weather stations.
1. Overview of Wireless Weather Stations
1.1 What is a Wireless Weather Station?
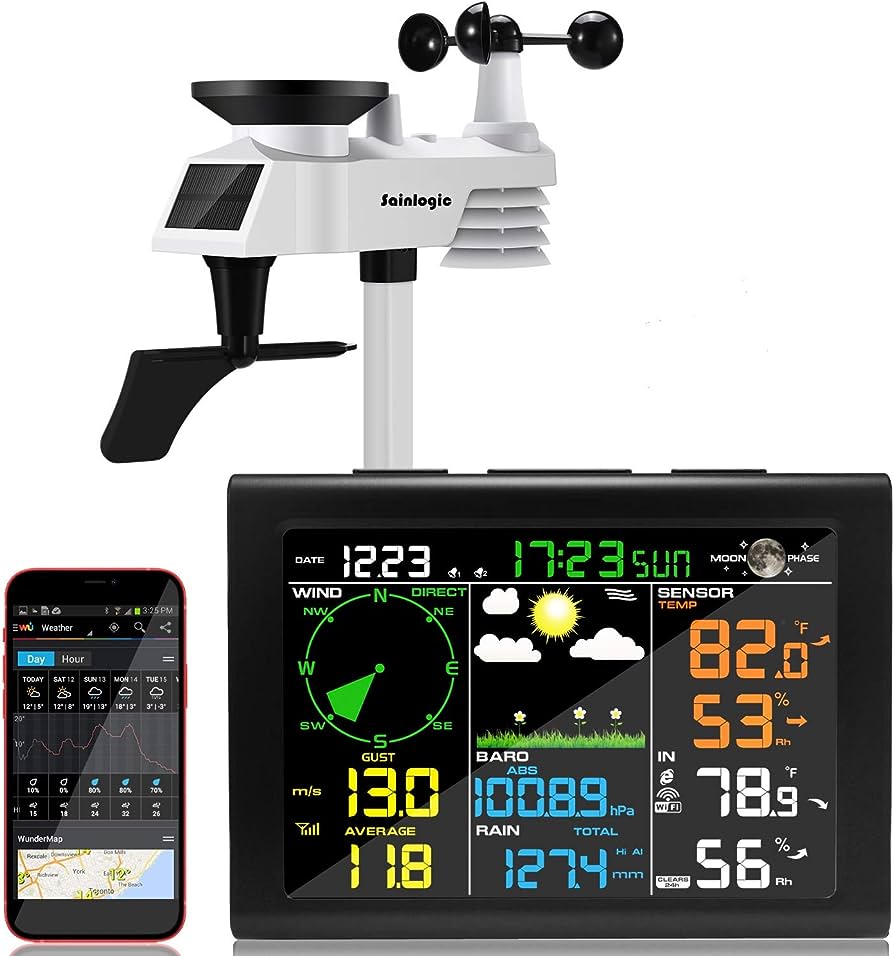
A wireless weather station is an advanced meteorological device that measures and monitors various weather conditions. Unlike traditional weather stations, which require wired connections for data transmission, wireless weather stations utilize wireless technology to collect and transmit weather data.
These stations have multiple sensors strategically placed to gather information on temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction, rainfall, and atmospheric pressure. This data is transmitted wirelessly to a display console or a computer, which can be analyzed and used to make informed weather-related decisions.
1.2 Importance and Benefits
Wireless weather stations provide accurate and real-time weather information to individuals, businesses, and government agencies. By monitoring weather conditions, these stations help forecast weather patterns, vital for planning outdoor activities, agricultural operations, and aviation activities.
Wireless weather stations also provide early warning systems for severe weather events such as hurricanes, tornadoes, or heavy rainfall. Additionally, these stations are helpful for climate researchers, meteorologists, and data enthusiasts who analyze weather patterns over time.
The benefits of using wireless weather stations are numerous. Firstly, their wireless nature eliminates the need for complicated wiring installations, making them easier to set up and maintain. They are portable, allowing you to move them around your property to measure weather conditions in different locations accurately.
Wireless weather stations also offer real-time data updates, enabling users to make timely decisions based on weather information. Another advantage is accessing weather information remotely through internet-enabled devices, providing convenience and flexibility.
1.3 Components of a Wireless Weather Station
A typical wireless weather station consists of several components that work together to collect, transmit, and analyze weather data. These components include:
- Sensor Array: This is the core of the weather station and typically includes sensors for temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction, rainfall, and atmospheric pressure.
- Data Transmitter: The data collected by the sensor array is wirelessly transmitted to the console or a computer using various communication technologies, such as radio frequency (RF) or wireless Internet.
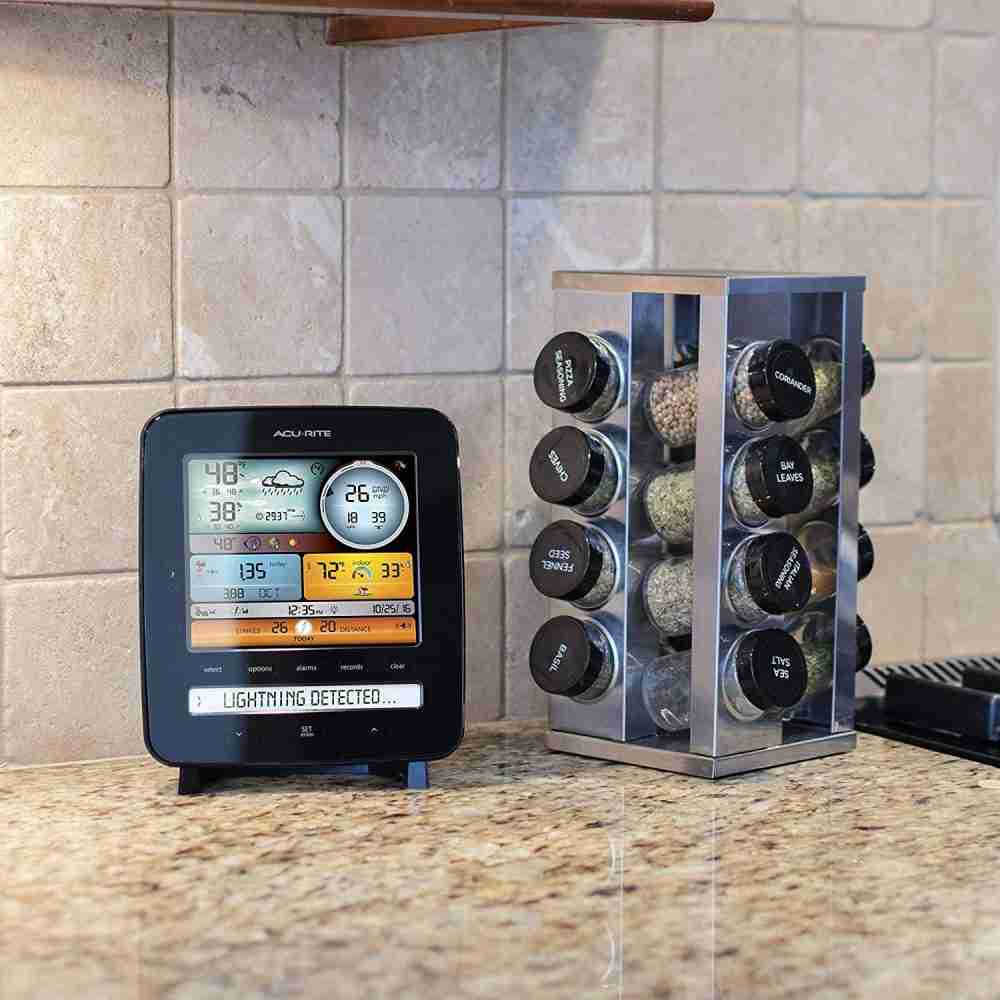
- Display Console: The console is the central hub for receiving and displaying weather data. It usually features a screen that shows real-time weather conditions and historical data, graphs, and charts.
- Software or Mobile App: Many wireless weather stations come with accompanying software or mobile apps, which allow users to visualize and analyze weather data, set up alerts, and access additional features.
- Power Source: The weather station components require a power source to operate. Depending on the specific model, this can be in batteries, solar power, or an AC power adapter.
- Mounting Hardware: To ensure accurate measurements, wireless weather stations often include mounting hardware that allows you to securely attach the sensor array to a suitable location, such as a pole or rooftop.
2. Basic Functionality of Wireless Weather Stations
2.1 Collecting Weather Data
The primary function of a wireless weather station is to collect weather data from its various sensors. These sensors are strategically positioned outdoors to gather accurate and reliable information on temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction, rainfall, and atmospheric pressure. The data collected by the sensors is then transmitted wirelessly to the display console or computer for further analysis.
2.2 Monitoring Weather Conditions
Wireless weather stations continuously monitor and update weather conditions in real time. This lets you stay informed about the current temperature, humidity levels, wind speeds, and other essential weather parameters. Monitoring weather conditions is especially crucial for outdoor activities, event planning, and other situations where weather conditions can impact safety and comfort.
2.3 Recording and Storing Weather Data
In addition to real-time monitoring, wireless weather stations are designed to record and store historical weather data. This data can be analyzed to identify weather patterns, trends, and historical records. Access to historical weather data is valuable for agricultural planning, research purposes, and even personal interest in tracking weather changes over time. Some weather stations can export data for further analysis using external software or online platforms.
3. Wireless vs. Wired Weather Stations
3.1 Main Differences
One of the primary differences between wireless and wired weather stations is the method of data transmission. Wired weather stations require physical connections, usually cables, to transmit data from the sensors to the display console or computer.
On the other hand, wireless weather stations utilize wireless communication technologies such as radio frequency (RF) or Wi-Fi to transmit data across distances without physical connectivity.
3.2 Advantages of Wireless Weather Stations
Wireless weather stations offer several advantages over their wired counterparts. Firstly, the absence of wiring installations simplifies the setup process, making wireless weather stations more user-friendly. This also allows for greater flexibility in sensor placement, enabling more accurate and diverse weather measurements. Wireless weather stations are also portable, making it easier to relocate them as needed.
Another significant advantage is the elimination of cable-related maintenance issues. Wired weather stations can experience problems such as cable damage, disconnections, or signal interference, leading to inaccurate or unreliable data. Wireless weather stations significantly reduce these issues, resulting in more consistent and high-quality weather data.
3.3 Advantages of Wired Weather Stations
While wireless weather stations have many benefits, there are situations where wired weather stations may be more suitable. Wired weather stations can provide a more reliable and stable connection, as they are not susceptible to interference or signal loss like wireless systems. This can be particularly important in areas with dense foliage, buildings, or other obstacles that may hinder wireless transmissions.
Additionally, wired weather stations do not rely on batteries or charging for power, as they are typically connected directly to a power source. This eliminates the need to replace or recharge batteries, ensuring continuous operation regularly. Wired weather stations are also less vulnerable to cyber-attacks or hacking since data transmission occurs through physical connections rather than wireless networks.
4. Wireless Weather Station Connectivity
4.1 Wireless Connection Options
Wireless weather stations utilize various connectivity options to transmit data from the sensors to the display console or computer. One standard method is radio frequency (RF) communication, where the sensor data is transmitted wirelessly over a short-range frequency. This is often used when there is a direct line of sight between the sensor and the receiver.
Another connectivity option is Wi-Fi, which allows the weather station to connect to an existing wireless network and transmit data to a computer or cloud-based platform. Wi-Fi connectivity offers greater flexibility and range, as line-of-sight restrictions do not limit it. However, successful communication requires a stable and reliable Wi-Fi network.
Some advanced wireless weather stations offer cellular connectivity, allowing them to connect to the Internet using a SIM card. This allows for remote monitoring and data access, even in locations where Wi-Fi connectivity is unavailable.
4.2 Transmission Range
The transmission range of wireless weather stations varies depending on the specific model and the communication technology used. Generally, most wireless weather stations range from 300 to 1000 feet (90 to 300 meters) for RF communication. However, this range can be affected by obstacles such as walls, trees, or other structures that can weaken the signal.
For Wi-Fi-enabled weather stations, the range is typically determined by the strength and coverage of the existing Wi-Fi network. In general, Wi-Fi networks can provide coverage up to a few hundred feet (60 to 90 meters) indoors and even longer distances outdoors, depending on the quality of the network equipment.
4.3 Interference and Signal Strength
Interference and signal strength are essential considerations when using wireless weather stations. Interference can occur when multiple devices or sources emit signals in the same frequency range, causing distortion or loss. This interference can be caused by nearby electronic devices, power lines, or obstacles obstructing the signal path.
Choosing a wireless weather station that operates on a frequency band with minimal interference is essential to ensure reliable and accurate data transmission. Some weather stations offer the option to select different frequency channels to avoid interference from nearby devices.
Signal strength is another crucial factor in wireless connectivity. A strong and stable signal ensures consistent and uninterrupted data transmission. Factors affecting signal strength include distance, obstacles, and the quality of the wireless technology used. To optimize signal strength, it is recommended to place the weather station sensors and receiver in locations with minimal obstacles and within the recommended transmission range.
5. The Role of the Internet in Wireless Weather Stations
5.1 Internet as a Communication Medium
The Internet plays a crucial role in the functionality of wireless weather stations, particularly in transmitting weather data to remote locations or accessing real-time updates. Weather stations with Wi-Fi or cellular connectivity can directly connect to the Internet, allowing users to access weather information from anywhere with an Internet connection.
Using the Internet as a communication medium offers several advantages. It allows for remote monitoring and data access, making it possible to check weather conditions even when you are away from home or the weather station’s location. Internet connectivity also enables the sharing of weather data with online communities or organizations, contributing to collective weather data analysis and forecasting.
5.2 Internet-Enabled Features
With internet connectivity, wireless weather stations can offer additional features and functionality. Some weather stations can integrate with online weather platforms or services, providing access to extended weather forecasts, historical data, or specialized insights. Internet-enabled weather stations may also offer features such as email or text message alerts for specific weather conditions, ensuring that you stay informed about any changes that may affect your activities or safety.
Furthermore, many weather stations can connect to personal weather websites or mobile apps, allowing you to create custom dashboards, view weather information on-demand, and share weather data with others. These internet-enabled features enhance the usability and accessibility of wireless weather stations, providing users with a more comprehensive weather monitoring experience.
5.3 Potential Limitations
While internet connectivity in wireless weather stations offers numerous benefits, it is essential to consider potential limitations. Internet-dependent functionalities rely on a stable and reliable internet connection. In areas with limited internet access or unstable network conditions, these features may not function optimally or may not be accessible at all. It is recommended to ensure that your internet connection is reliable and that your weather station is compatible with your network setup before relying heavily on internet-dependent features.
Another potential limitation is the need for cloud-based services or third-party platforms to access and interpret weather data. While these services are often user-friendly and provide valuable insights, they may require additional subscriptions or ongoing fees for full access to their features. It is essential to consider the associated costs and terms of use when choosing an internet-enabled weather station.
6. Weather Station Software and Mobile Apps
6.1 Data Display and Analysis
To make the most of your wireless weather station, manufacturers often provide software or mobile apps. These software applications provide a user-friendly interface to visualize, analyze, and interpret weather data the weather station collects. The software typically displays real-time weather conditions, historical data, and various graphs and charts to help you understand and interpret weather patterns.
Weather station software enables you to create custom dashboards, set up personalized alerts, and track weather changes over time. Some advanced software even offers more advanced features like data export to external programs for further analysis or integration with other smart home devices.
6.2 Remote Access and Control
Another valuable feature of weather station software and mobile apps is remote access and control. With an internet-enabled weather station, you can access the weather data remotely using your computer, smartphone, or tablet. This allows you to check weather conditions, review historical data, and adjust your weather station settings from anywhere with an internet connection.
Remote access can be handy for frequent travelers, agricultural operations, or industries that require real-time weather monitoring across different locations. It ensures you are always connected to your weather station and can make informed decisions based on the most up-to-date weather information.
6.3 Compatible Platforms
When choosing a wireless weather station, it is essential to consider the compatibility of the accompanying software or mobile app with your preferred platforms. Weather station software and apps are typically available for Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android platforms. However, compatibility can vary depending on the manufacturer and model.
It is recommended to check the system requirements and app availability before purchasing. Choosing a weather station with software/app compatibility across multiple platforms ensures that you can access and analyze your weather data no matter your preferred device.
7. Internet-Dependent Features in Wireless Weather Stations
7.1 Real-Time Data Updates
One of the notable features of internet-enabled wireless weather stations is the ability to receive real-time data updates. These stations can transmit weather data to online weather platforms or personal weather websites, allowing users to access real-time weather information remotely.
Real-time data updates are particularly beneficial for users who require up-to-the-minute weather information for planning outdoor activities, research, or safety purposes. You can make informed decisions and adjust your plans by receiving accurate and timely weather updates.
7.2 Weather Data Sharing
Internet-connected weather stations can also share weather data with online communities or weather organizations. This sharing of weather data contributes to collective weather analysis, forecasting accuracy, and climate research.
Weather enthusiasts can participate in citizen science projects, where individuals contribute their weather data to a more extensive database for further analysis. Sharing your weather data can also help create local weather networks, where multiple weather stations work together to provide more extensive weather coverage in a particular area.
7.3 Integration with Smart Home Systems
Another advantage of internet-connected wireless weather stations is the integration with smart home systems. Connecting your weather station to a smart home platform can trigger automated actions based on specific weather conditions.
For example, you can program your smart home system to automatically adjust the thermostat or control window shades based on the detected temperature or sunlight intensity. This integration enhances the convenience and efficiency of your smart home, creating a more comfortable and sustainable living environment.
8. Offline Functionality and Memory
8.1 Data Storage and Retrieval
Even though internet connectivity offers numerous benefits, the ability of a wireless weather station to function offline is also crucial. In situations where internet access is unavailable, having offline functionality ensures continuous data logging and monitoring. Weather stations typically have built-in memory or data storage capabilities to record and store weather data for later retrieval.
When the weather station regains connectivity, the stored data can be synchronized with the online platform or software for analysis and further processing. This offline functionality ensures that weather data is not lost during intermittent internet access.
8.2 Backup Power
Wireless weather stations often rely on batteries or solar power for operation. A reliable backup power source is essential to ensure uninterrupted functionality, especially during power outages or periods of low solar energy. Battery backup systems or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) can provide temporary power to the weather station components, ensuring continuous data collection and transmission.
Having a backup power source is particularly important in areas prone to frequent power outages or in situations where continuous monitoring is critical, such as weather-related emergency preparedness or research applications.
8.3 Offline Monitoring
Even without an internet connection, wireless weather stations can provide immediate and local weather data. The display console or mobile app associated with the weather station allows you to monitor real-time weather conditions directly without relying on online data updates.
This offline monitoring capability can be valuable when a stable internet connection is unavailable, such as in remote locations or temporary deployments. It ensures that you have access to critical weather information, regardless of the availability of an internet connection.
9. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Wireless Weather Station
9.1 Need for Internet Connectivity
When selecting a wireless weather station, you must consider your specific internet connectivity requirements. If remote access, real-time updates, and online features are essential, choose a weather station with reliable internet and Wi-Fi or cellular connectivity options. However, a station with offline functionality and robust memory capacity may be more suitable if you prefer local monitoring and data storage without relying heavily on internet connectivity.
9.2 Desired Features
Identify the key features and capabilities when choosing a wireless weather station.
Consider the types of weather data you want to monitor, the range and accuracy of the sensors, and the level of customization and analysis provided by the accompanying software or mobile app. Consider additional features, such as weather alerts, integration with other devices or platforms, and compatibility with your preferred operating system.
9.3 Budget and Cost Considerations
Wireless weather stations vary significantly in terms of cost and functionality. Set a budget and consider the long-term costs associated with the weather station, such as subscription fees for online services or replacement batteries.
While investing in a reliable and accurate weather station is important, choosing one that aligns with your budget and provides the necessary features to meet your specific needs is also essential.
10. Conclusion
10.1 Summary of Key Points
Wireless weather stations are advanced meteorological devices that utilize wireless technology to collect, transmit, and analyze weather data. These stations have multiple sensors to measure temperature, humidity, wind speed and direction, rainfall, and atmospheric pressure.
They offer real-time weather monitoring, historical data recording, and various remote access and control connectivity options. Internet-enabled features provide extended functionality such as real-time data updates, weather data sharing, and integration with smart home systems.
10.2 Making an Informed Decision
When choosing a wireless weather station, it is essential to consider factors such as the need for internet connectivity, desired features, budget, and cost considerations. Understanding the differences between wireless and wired weather stations, as well as the advantages and limitations of internet-enabled weather stations, can help you make an informed decision that best suits your weather monitoring needs.
Whether you are a weather enthusiast, a researcher, or simply looking to stay informed about the local weather, a wireless weather station can offer valuable insights and enhance your understanding of the ever-changing weather conditions.