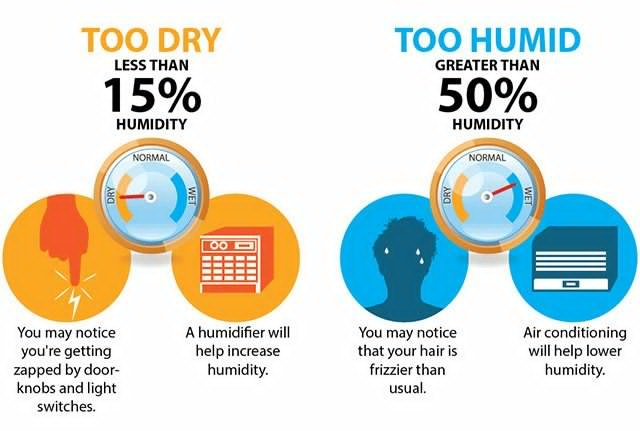
In this article, you will explore the concept of humidity percentage and gain a clear understanding of what it means.
We will also uncover the definition of high humidity and its potential effects.
Additionally, we will touch upon the role of a humidifier in maintaining optimal humidity levels.
By the end, you will be well-informed about humidity and its significance in your everyday life. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey to discover the mysteries of humidity together!
Review contents
Understanding Humidity Percentage
Definition of Humidity
Humidity refers to the amount of moisture present in the air. It measures water vapor in the air and is crucial in determining how comfortable or uncomfortable the environment feels.
The humidity level is generally expressed as a percentage known as the humidity percentage.
Calculating Humidity Percentage
The humidity percentage is calculated by measuring the amount of moisture in the air relative to the maximum amount of moisture the air can hold at a specific temperature.
This calculation is known as relative humidity. The formula for calculating relative humidity considers the actual and saturation vapor pressure at a given temperature.
Relative Humidity vs. Absolute Humidity
Relative humidity is the most commonly used measurement of humidity, as it relates the amount of moisture in the air to the maximum amount the air can hold at a specific temperature.
Absolute humidity, however, measures the actual amount of moisture in the air, regardless of temperature. While relative humidity is a more practical measure for everyday use, absolute humidity is often used in scientific and engineering applications.
Factors Influencing Humidity
Temperature
Temperature plays a significant role in determining the humidity level. Warmer air has a higher capacity for holding moisture, which can contain more water vapor.
As the temperature increases, the air can hold more moisture without becoming saturated, leading to higher humidity levels. Conversely, cooler air has a lower capacity for moisture, resulting in lower humidity levels.
Weather Conditions
Weather conditions like rainfall, fog, and snow can significantly influence humidity. Rainfall and snowfall add moisture to the air, increasing humidity.
Fog occurs when the air becomes saturated with moisture, resulting in high humidity levels. Understanding weather patterns and their impact on humidity can help manage and adjust indoor humidity levels accordingly.
Proximity to Water Bodies
The proximity to large water bodies, such as oceans, lakes, or rivers, can significantly affect humidity levels. Areas close to water bodies tend to have higher humidity levels due to the evaporation of water into the air.
As the water evaporates, it adds moisture to the surrounding air, increasing the humidity. This phenomenon is often observed in coastal regions and cities near lakes or rivers.
Effects of High Humidity
Discomfort and Health Issues
High humidity levels can lead to discomfort and various health issues. When humidity is too high, it can make the air feel heavy and damp, causing discomfort and difficulty in breathing.
Excessive moisture in the air can also contribute to the growth of certain bacteria, fungi, and dust mites, exacerbating respiratory problems and allergies. Additionally, high humidity can make it harder for sweat to evaporate from the body, leading to feelings of stickiness and increased perception of heat.
Damage to Property
High humidity can have detrimental effects on property. Excessive moisture in the air can cause wooden furniture, floors, and musical instruments to warp or swell. It can also lead to peeling paint and wallpaper, mold growth, and mildew on walls and ceilings.
Electronic devices and appliances can be affected by high humidity, leading to malfunctions and reduced lifespan. Furthermore, high humidity can cause damage to books, photographs, and other paper-based materials.
Promotion of Mold and Dust Mites
High humidity provides the ideal conditions for the growth of mold and dust mites. Mold thrives in damp environments and quickly spreads on walls, ceilings, and fabrics.
It causes unsightly stains and releases spores that can trigger allergic reactions and respiratory problems. Dust mites, microscopic creatures that live in dust and thrive in humid conditions, can also contribute to allergies and respiratory issues.
Ideal Humidity Levels
Indoor Humidity Recommendations
Maintaining an optimal humidity level indoors is essential for comfort and health. The ideal indoor humidity level typically falls between 30% and 50%. In colder climates, a range between 30% and 40% is recommended to prevent condensation and mold growth.
A range between 40% and 50% is recommended in warmer climates to balance comfort and moisture control. It is essential to monitor and adjust indoor humidity levels accordingly, especially during seasons with extreme temperatures.
Outdoor Humidity Guidelines
While it is impossible to control outdoor humidity levels, being aware of them can help manage indoor humidity effectively. Outdoor humidity levels vary depending on geographical location, climate, and weather conditions.
In general, outdoor humidity tends to be higher during warmer seasons and in areas near water bodies. Monitoring weather forecasts and local climate patterns can provide insight into outdoor humidity levels, assisting in maintaining indoor humidity within the recommended range.
Defining High Humidity
Threshold for High Humidity
There is no universal threshold for high humidity, as optimal humidity levels can vary depending on personal comfort and geographical location.
However, it is generally considered that relative humidity levels above 60% can be classified as high humidity. This higher humidity range may result in discomfort, condensation, and an increased risk of mold growth.
Dangers of Excessive Humidity Levels
Excessive humidity levels can pose various dangers to human health and property. High humidity can impede the body’s ability to cool down through the evaporation of sweat, potentially leading to heat exhaustion or heatstroke.
It can also contribute to the growth of mold, which can cause allergies and respiratory issues. Furthermore, excessive humidity can result in structural damage to buildings, furniture, and electronic devices.
Signs of High Humidity
Physical Discomfort
One of the most noticeable signs of high humidity is the physical discomfort experienced in the environment. When high humidity levels, the air can feel heavy and stifling, making breathing difficult. People may feel sticky or sweaty even without physical exertion. Increased perspiration and difficulty regulating body temperature are common symptoms of high humidity.
Condensation
Condensation is another visible sign of high humidity. When warm, humid air comes into contact with more excellent surfaces, the moisture in the air condenses and forms water droplets. This can be seen on windows, mirrors, and cold surfaces like metal or ceramic. Condensation can also occur on walls and ceilings, promoting the growth of mold and mildew.
Musty Odors
High humidity can produce musty odors in indoor spaces. The excess moisture in the air can lead to the growth of mold and mildew, which release distinct odors.
These odors are often described as earthy or damp and can permeate through the affected area. Musty odors are not only unpleasant but can also signify the presence of mold, which can be harmful to health.
Managing High Humidity
Humidity Control Tips
Several ways exist to manage and control high humidity levels in indoor spaces. One effective method is to use air conditioning or dehumidifiers to remove excess moisture from the air.
Regularly checking and emptying water collection trays in dehumidifiers is essential to prevent mold growth. Fans or opening windows to create airflow can also help reduce humidity levels.
Using Dehumidifiers
Dehumidifiers are specifically designed to extract moisture from the air, helping to maintain optimal humidity levels. These devices work by drawing in humid air, cooling it to condense the moisture, and releasing drier air into the environment. Dehumidifiers can be particularly useful in areas with consistently high humidity, such as basements, bathrooms, and laundry rooms.
Ventilation and Air Circulation
Improving ventilation and promoting air circulation can help in managing high humidity. Opening windows and using ceiling fans or portable fans can help exchange humid air with fresh, drier air from outside.
Proper airflow can also prevent moisture buildup in closed spaces, reducing the risk of mold growth. Regularly cleaning and maintaining air vents and ducts can ensure adequate airflow throughout the building.
Humidity and Health
Respiratory Issues
High humidity can have various impacts on respiratory health. Excessive moisture in the air can create an environment conducive to mold growth, which releases spores that can trigger allergies, asthma, and other respiratory conditions.
Additionally, high humidity can make it more difficult for individuals with respiratory issues to breathe comfortably, exacerbating symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Skin Problems
High humidity can affect the skin by interfering with its natural moisture balance. The increased moisture in the air can cause the skin to feel sticky and damp, making it more susceptible to rashes, acne breakouts, and fungal infections.
In some cases, the excess moisture can also lead to the proliferation of certain bacteria, contributing to skin irritation and inflammation.
Potential Allergies
High humidity levels can trigger allergies in susceptible individuals. Dust mites, mold spores, and other allergens thrive in humid environments and can cause allergic reactions such as sneezing, itching, and watery eyes.
Individuals with allergies or sensitivities to these allergens may experience increased symptoms when exposed to high humidity.
Impact of High Humidity on Electronics
Corrosion
High humidity can have damaging effects on electronic devices and appliances. The excess moisture in the air can lead to condensation on circuit boards and other components, causing corrosion.
Corrosion can result in the degradation of electrical connections and hinder the proper functioning of electronic devices.
Malfunctioning
Electronic devices are designed to operate within specific temperature and humidity ranges. When exposed to high humidity, these devices may experience malfunctions or failures. Moisture can cause short circuits, damage sensitive components, and interfere with electrical signals, resulting in erratic behavior or complete failure of the device.
Reduced Lifespan
The lifespan of electronic devices can be significantly reduced in high-humidity environments. The air’s moisture can accelerate the components’ aging process, leading to premature wear and degradation. The increased risk of corrosion and malfunctions further contributes to the shortened lifespan of electronic devices.
Preventing High Humidity
Moisture-Proofing Measures
To prevent high humidity levels, moisture-proofing measures should be implemented. This includes sealing cracks and gaps in walls and windows to prevent moisture infiltration. Applying waterproof coatings or paints to surfaces can also help reduce moisture absorption. Additionally, installing moisture barriers, such as vapor barriers, can prevent moisture from entering the building through the foundation or floors.
Routine Maintenance and Inspections
Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify and address sources of high humidity. Checking for leaks in plumbing fixtures, roofs, and windows can prevent the entry of excess moisture into the building.
Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial in controlling humidity levels. Ensuring that all building areas are well-ventilated can help reduce moisture buildup. Installing exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms can effectively remove excess moisture from cooking and bathing.
Opening windows and using fans can promote cross-ventilation, exchanging humid air with fresh air from the outside.
ThermoPro TP50 Digital Hygrometer Indoor Thermometer Room Thermometer and Humidity Gauge with Temperature Monitor
$9.34 in stock
10 used from $9.89
ThermoPro TP49 Digital Hygrometer Indoor Thermometer Humidity Meter Room Thermometer with Temperature and Humidity Monitor Mini Hygrometer Thermometer
$8.99 in stock
1 used from $8.79
Antonki Room Thermometer for Home, 2 Pack Digital Temperature and Humidity Monitors, Indoor Hygrometer Sensor, Humidity Gauge, Humidity Meter for Baby Room, Terrarium, Incubator, Greenhouse
$8.49 in stock
Govee Hygrometer Thermometer H5075, Bluetooth Indoor Room Temperature Monitor Greenhouse Thermometer with Remote App Control, Notification Alerts, 2 Years Data Storage Export,LCD
$12.99 in stock
ThermoPro TP49 3 Pieces Digital Hygrometer Indoor Thermometer Humidity Meter Mini Hygrometer Thermometer with Temperature and Humidity Monitor Room Thermometer
$19.99 in stock
1 used from $20.18